Anti-Aging Therapy FAQ
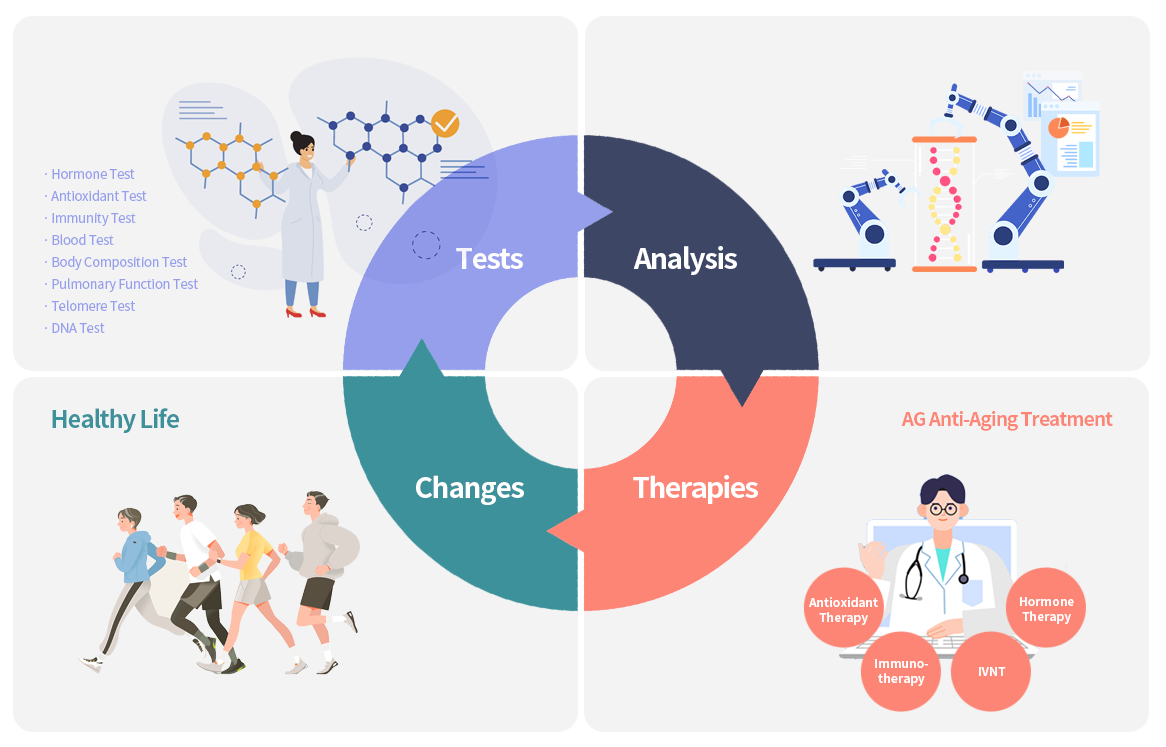
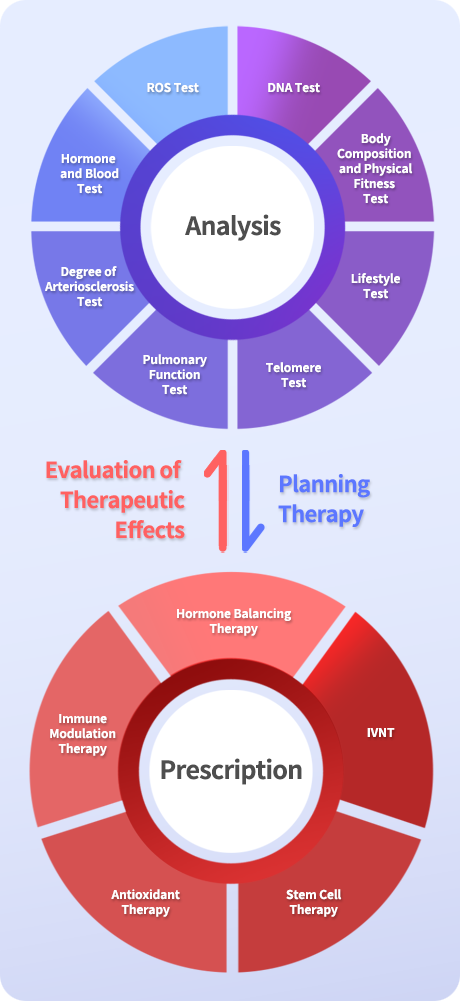
Anti-aging treatment typically requires ongoing, continuous treatment rather than a one-time procedure. This is because aging is a complex process that involves multiple factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors, and there is no single intervention that can stop or reverse the aging process entirely. Instead, anti-aging treatment typically involves a combination of interventions that are tailored to an individual's unique needs and health status. These interventions may include: Lifestyle modifications: This may include exercise, healthy diet, stress management, and adequate sleep. Skin care: This may include the use of topical treatments such as moisturizers, retinoids, and sunscreen to protect and nourish the skin. Hormone balancing therapy: This may involve the use of hormone replacement therapy to address imbalances in hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, and thyroid hormones. Nutritional supplements: This may include supplements such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can support overall health and promote healthy aging. Medical treatments: This may include treatments such as stem cell therapy or regenerative medicine to promote tissue repair and regeneration. While some anti-aging interventions may provide immediate benefits, most require ongoing treatment and maintenance to achieve optimal results. For example, exercise and a healthy diet may provide immediate benefits such as improved energy and mood, but these benefits may diminish over time if the individual does not maintain these habits. Overall, anti-aging treatment is a continuous process that requires ongoing attention to lifestyle, nutrition, and medical interventions in order to promote healthy aging and optimize overall health and well-being.
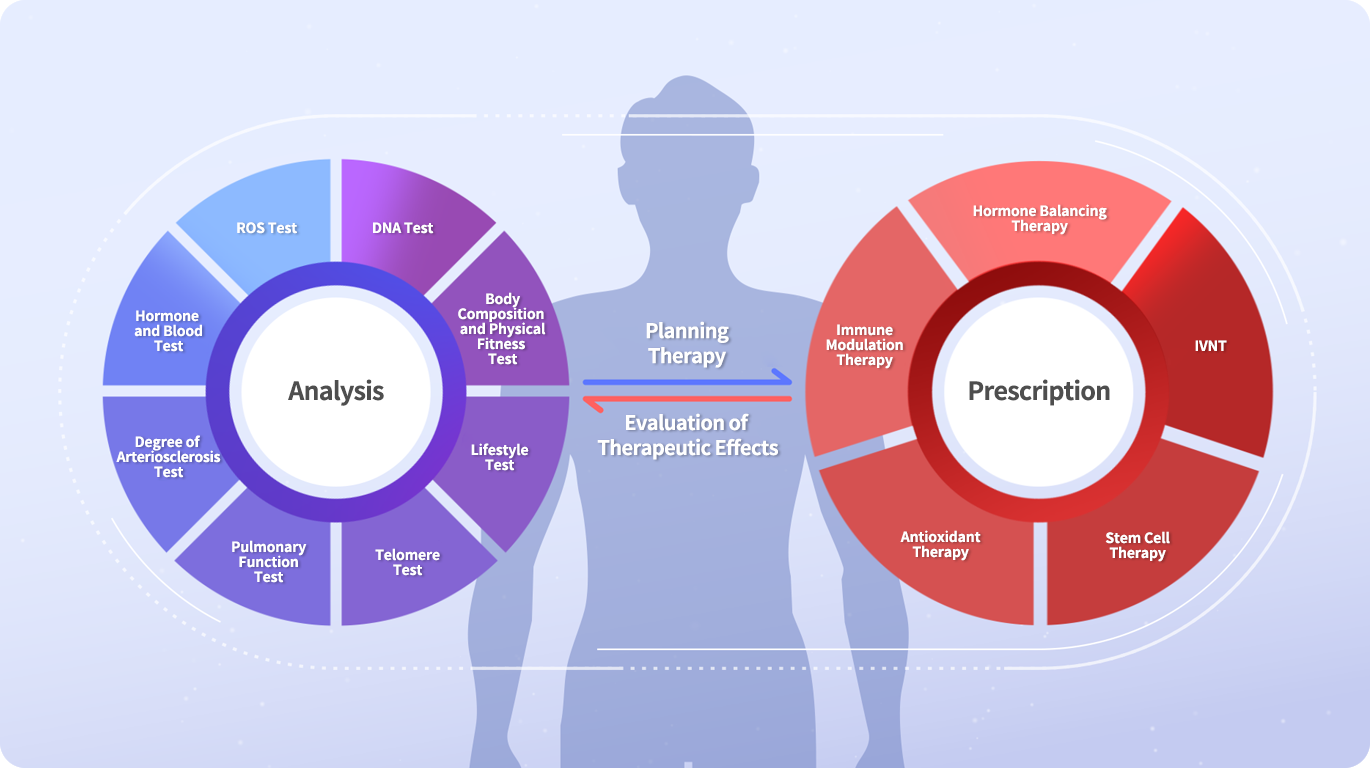
Personalized treatment in anti-aging is important because every individual ages differently, with different genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors contributing to the aging process. Therefore, a one-size-fits-all approach to anti-aging is unlikely to be effective for everyone. Personalized treatment takes into account an individual's unique characteristics and medical history, and tailors anti-aging interventions to their specific needs and health concerns. This may involve a combination of treatments, such as lifestyle modifications, supplements, and medications, that are selected based on an individual's unique profile and medical history. Personalized treatment can also help to identify and address underlying health problems that may be contributing to the aging process. For example, a healthcare professional may recommend testing for hormone imbalances or nutrient deficiencies that could be affecting an individual's overall health and contributing to the aging process. Finally, personalized treatment can also help to monitor the effectiveness of anti-aging interventions over time, and make adjustments as needed based on an individual's response. This can help to optimize treatment outcomes and improve overall health and quality of life. Overall, personalized treatment in anti-aging is important because it takes into account the unique characteristics of each individual and tailors treatment interventions to their specific needs and health concerns. This approach can help to optimize treatment outcomes and promote healthy aging.
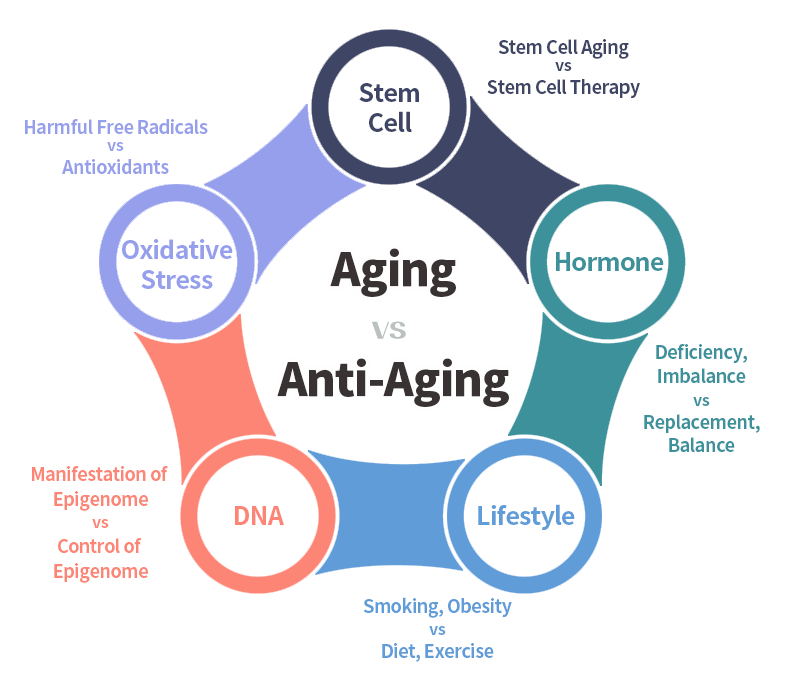
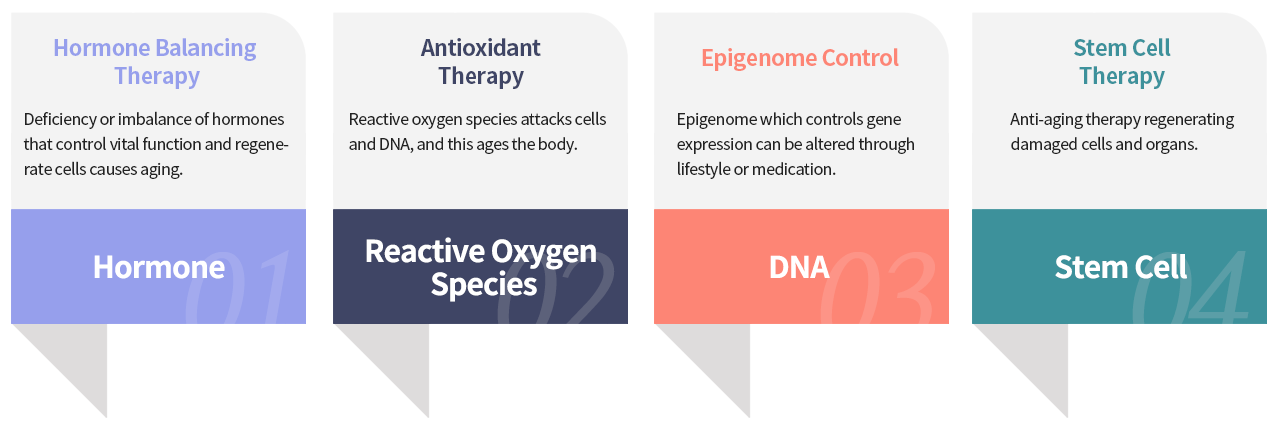
Integrated treatment is important in anti-aging because the aging process involves multiple factors that interact with each other, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Therefore, an integrated approach that addresses these multiple factors is more likely to be effective in promoting healthy aging and preventing age-related diseases. An integrated approach to anti-aging may include a combination of treatments, such as: Nutrition and exercise: A healthy diet and regular exercise can help to promote healthy aging by reducing inflammation, improving immune function, and maintaining muscle mass and bone density. Hormone balancing therapy: As we age, our hormone levels naturally decline, which can contribute to age-related health problems. Hormone replacement therapy can help to restore hormone levels and improve symptoms of hormone imbalances. Anti-aging skincare: Skincare can help to protect the skin from damage caused by environmental factors and aging, such as UV radiation and oxidative stress. Stress management: Chronic stress can contribute to aging by increasing inflammation and oxidative stress. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help to reduce stress and promote healthy aging. Supplements and medications: Certain supplements and medications, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, may help to slow the aging process and prevent age-related diseases. Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell treatment is a type of medical treatment to repair or regenerate damaged tissues or organs. Stem cells are unique cells in the body that can divide and differentiate into many different types of cells, such as blood cells, nerve cells, and muscle cells. An integrated approach to anti-aging can help to address the multiple factors that contribute to aging and promote healthy aging. It's important to work with a healthcare professional who can help to Why do you need personalized treatment in Anti-aging? Personalized treatment in anti-aging is important because every individual ages differently, with different genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors contributing to the aging process. Therefore, a one-size-fits-all approach to anti-aging is unlikely to be effective for everyone. Personalized treatment takes into account an individual's unique characteristics and medical history, and tailors anti-aging interventions to their specific needs and health concerns. This may involve a combination of treatments, such as lifestyle modifications, supplements, and medications, that are selected based on an individual's unique profile and medical history. Personalized treatment can also help to identify and address underlying health problems that may be contributing to the aging process. For example, a healthcare professional may recommend testing for hormone imbalances or nutrient deficiencies that could be affecting an individual's overall health and contributing to the aging process. Finally, personalized treatment can also help to monitor the effectiveness of anti-aging interventions over time, and make adjustments as needed based on an individual's response. This can help to optimize treatment outcomes and improve overall health and quality of life. Overall, personalized treatment in anti-aging is important because it takes into account the unique characteristics of each individual and tailors treatment interventions to their specific needs and health concerns. This approach can help to optimize treatment outcomes and promote healthy aging.
Immune modulation refers to the ability to modify the activity of the immune system, either by enhancing or suppressing its response, in order to treat or prevent a disease. The immune system is responsible for defending the body against infections and other harmful substances, but in some cases, it can also attack healthy tissues and cause autoimmune disorders. Immune modulation can help to regulate the immune system and prevent it from attacking healthy tissues or boost the immune response to fight off infections and cancer. There are several ways to modulate the immune system, including through the use of immunomodulatory drugs, such as corticosteroids or biologics, or through natural methods, such as diet and exercise. Some other examples of immune modulation include vaccination, which stimulates the immune system to produce protective antibodies against specific pathogens, and immunotherapy, which uses drugs or other agents to activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. Immune modulation has the potential to be used in the treatment of a wide range of diseases, including autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and cancer. However, the effectiveness of immune modulation strategies can vary depending on the individual and the specific disease being treated. It's important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate immune modulation approach for each person.
Antioxidants are compounds that can help protect the body from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Free radicals are generated naturally in the body as a byproduct of normal metabolism, but they can also be produced by exposure to environmental factors like pollution, cigarette smoke, and radiation. When free radicals build up in the body, they can damage cells and contribute to a variety of health problems, such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer's disease. Antioxidants help to neutralize free radicals by donating an electron to them, which stabilizes them and prevents them from causing damage to cells. Some common antioxidants include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and selenium. These antioxidants can be found in many foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains. Some of the best food sources of antioxidants include blueberries, spinach, kale, dark chocolate, and nuts like almonds and walnuts.
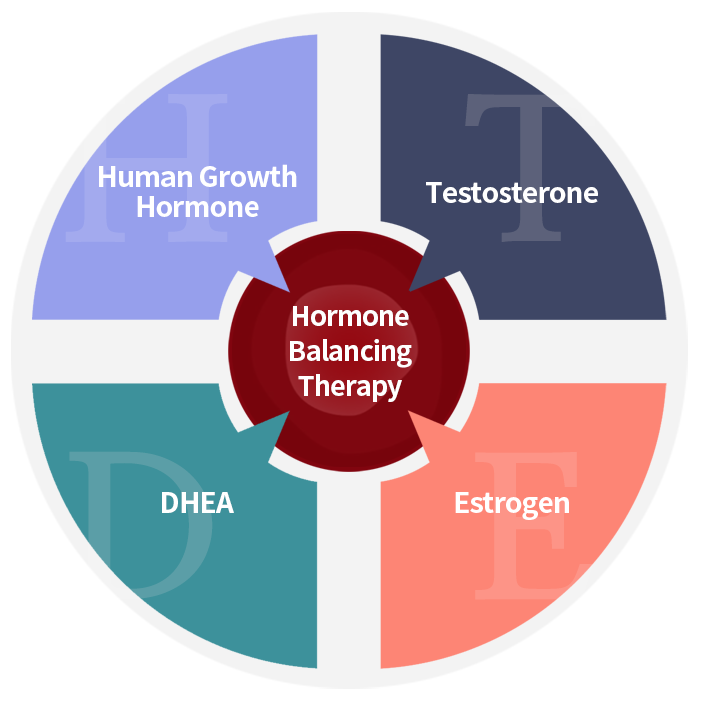
Hormone balancing therapy, also known as hormone replacement therapy, can have potential side effects, just like any other medical treatment. The specific side effects depend on the type of hormone being used, the dosage, and the individual's response to treatment. Some of the potential side effects of hormone balancing therapy include: Breast tenderness or swelling Mood changes, such as depression or irritability Fluid retention and weight gain Headaches Nausea and digestive issues Increased risk of blood clots, stroke, or heart attack It's important to note that the risk of side effects can vary depending on the specific hormone being used, as well as the individual's medical history and other risk factors. For example, estrogen therapy may increase the risk of blood clots or breast cancer in some individuals, while testosterone therapy may increase the risk of prostate cancer. To minimize the risk of side effects, it's important to work with a healthcare professional who is experienced in hormone balancing therapy and can help to determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration based on an individual's medical history and health status. It's also important to have regular follow-up appointments to monitor for potential side effects and adjust treatment as needed. Hormone balancing therapy, also known as hormone replacement therapy, can have potential side effects, just like any other medical treatment. The specific side effects depend on the type of hormone being used, the dosage, and the individual's response to treatment. Some of the potential side effects of hormone balancing therapy include: Breast tenderness or swelling Mood changes, such as depression or irritability Fluid retention and weight gain Headaches Nausea and digestive issues Increased risk of blood clots, stroke, or heart attack It's important to note that the risk of side effects can vary depending on the specific hormone being used, as well as the individual's medical history and other risk factors. For example, estrogen therapy may increase the risk of blood clots or breast cancer in some individuals, while testosterone therapy may increase the risk of prostate cancer. To minimize the risk of side effects, it's important to work with a healthcare professional who is experienced in hormone balancing therapy and can help to determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration based on an individual's medical history and health status. It's also important to have regular follow-up appointments to monitor for potential side effects and adjust treatment as needed.
The symptoms of hormone imbalances can vary depending on the specific hormones involved and whether they are overproduced or underproduced. Here are some general examples of symptoms that can be associated with hormone imbalances: Changes in appetite or weight gain/loss Fatigue or low energy Mood changes, such as depression or anxiety Changes in sex drive or fertility Insomnia or difficulty sleeping Hot flashes or night sweats Irregular menstrual periods or other menstrual changes Decreased muscle mass or bone density Dry skin or hair loss Increased or decreased sweating. Hormone imbalances can occur due to a variety of factors, including aging, stress, certain medical conditions, and exposure to environmental toxins. It's important to see a healthcare professional if you suspect you may have a hormone imbalance, as they can help to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include lifestyle changes, medications, or hormone replacement therapy.
Sex hormones are hormones that are responsible for the development and maintenance of sexual characteristics in males and females. The main sex hormones are testosterone and estrogen. In males, the primary sex hormone is testosterone, which is produced in the testes. Testosterone is responsible for the development of male sexual characteristics, such as increased muscle mass, facial hair, and a deep voice. Testosterone also plays a role in sperm production and sex drive. In females, the primary sex hormones are estrogen and progesterone, which are produced in the ovaries. Estrogen is responsible for the development of female sexual characteristics, such as breast growth and the widening of hips. Estrogen also plays a role in the menstrual cycle and bone health. Progesterone is primarily involved in preparing the uterus for pregnancy and maintaining a healthy pregnancy. In addition to their primary roles in sexual development and reproduction, sex hormones also play a role in other bodily functions, such as bone health, metabolism, and mood regulation. Imbalances in sex hormone levels can lead to a variety of health problems, such as infertility, osteoporosis, and mood disorders.
Growth hormone (GH), also known as somatotropin, is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that plays a crucial role in regulating growth, metabolism, and body composition. In children and adolescents, growth hormones are essential for normal growth and development, stimulating the growth of bones, muscles, and organs. In adults, growth hormones help to maintain muscle mass and bone density, regulate body fat, and support overall health and well-being. The secretion of growth hormones is regulated by several factors, including sleep, exercise, stress, and nutrition. Growth hormone levels are typically highest during childhood and adolescence, and gradually decline as we age. Deficiencies or excesses in growth hormones can lead to a range of health problems. Growth hormone deficiency can cause stunted growth and development in children, while in adults, it can lead to decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and reduced bone density. Excess levels of growth hormone can cause a condition called acromegaly, which is characterized by the overgrowth of bones and tissues, as well as other health problems such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands, such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas, among others, that are responsible for regulating various physiological processes in the body. Hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and travel throughout the body to specific target cells, where they bind to specific receptor proteins and initiate a signaling pathway that leads to a specific biological response. Hormones play a critical role in many bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and the regulation of the immune system. Hormone levels can be affected by a variety of factors, such as stress, diet, and exercise, and imbalances in hormone levels can lead to a variety of health problems, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and infertility.